Unofficial Actors in the Policy Process
Actor Interaction
POSC 315: Week 4-2
Overview
- Unofficial Actors
- News Media
- Political Parties
- Interest Groups
- Think Tanks
- Corporations
- Individuals
- Concepts of Interaction
The News Media
"Politicians and the news media create a world of political fictions by developing causal stories that determine to whom and to where or to what blame is affixed." - Deborah Stone
Media Framing
Key Concepts
- Frame definition: "The process by which a communication source defines and constructs a political issue or public controversy"
- Impact on public perception
- Example: "Immigrant Caravan" vs. "Refugee Caravan"
Media Gatekeeping
- Control over story selection
- Editorial decisions
- Story placement
- Coverage duration
- Impact on policy windows
- Creating opportunities
- Sustaining attention
- Influencing timing
Modern Media Dynamics
- Evolution of Media Landscape
- Traditional vs. Digital platforms
- Social media impact
- 24-hour news cycle
- Challenges
- Decreasing attention spans
- Information overload
- Echo chambers
Pack Journalism
"The tendency of journalists to cover the same stories in the same way because they are competing with each other for audience attention."
- Creates story momentum
- Reinforces narrative frames
- Can lead to groupthink
Political Parties
Unique characteristics:
- Not mentioned in Constitution
- Created by politicians
- Essential for ballot access
Party Functions
- Coordination Functions
- Coordinate actions
- Communicate with voters
- Raise money
- Recruit candidates
- Mobilize voters
- Organize government
Modern Party Dynamics
- Polarization Effects
- Increased ideological sorting
- Gridlock challenges
- Partisan policy formation
- Institutional Changes
- Primary system evolution
- Campaign finance role
- Party discipline
Party Realignment
Historical Examples
- The New Deal Coalition
- Southern Strategy
- Reagan Revolution
Interest Groups
Core Definitions
- "An organization that tries to influence public policy decisions." - Stone
- "A collection of individuals who share a common interest or attitude and seek to influence government for specific ends." - Lowi
Interest Group Types
- Institutional Groups
- National Governors Association
- National League of Cities
- National Association of Counties
- Economic Groups
- National Association of Manufacturers
- American Petroleum Institute
- American Medical Association
- Public Interest Groups (PIGs)
- Sierra Club
- National Rifle Association
- Consumer advocacy organizations
Modern Interest Group Strategies
Digital Age Tactics
- Social Media Campaigns
- Viral advocacy
- Online mobilization
- Digital grassroots
- Data-Driven Approaches
- Targeted messaging
- Analytics-based advocacy
- Digital engagement metrics
Interest Group Activities
- Direct Activities
- Lobbying
- Campaign contributions
- Litigation
- Venue shopping
- Indirect Activities
- Public relations
- Grassroots mobilization
- Coalition building
- Research and education
AstroTurfing
Modern Examples
- Definition: Creating artificial grassroots movements
- Current Examples:
- Industry-funded citizen groups
- Corporate-sponsored local movements
- Social media manipulation campaigns
- Impact on Policy Process
- Public perception manipulation
- Policy agenda influence
- Legislative pressure
Think Tanks
Research and advocacy organizations focusing on:
- Policy research
- Analysis
- Recommendations
- Public education
Think Tank Categories
- Academic Think Tanks
- Brookings Institution
- RAND Corporation
- Advocacy Think Tanks
- Heritage Foundation
- Center for American Progress
- Contract Research Organizations
- Urban Institute
- Research Triangle Institute
Think Tank Influence
- Policy Research
- Data analysis
- Policy evaluation
- Impact assessment
- Knowledge Translation
- Policy briefs
- Media engagement
- Decision-maker outreach
Think Tank Funding
Funding Sources
- Private Donors
- Foundations
- Corporations
- Government Contracts
- Endowments
Impact on Research Focus and Credibility
Corporations and Business
Policy Process Role
- Direct policy influence
- Economic stakeholders
- Implementation partners
- Resource providers
Corporate Policy Tools
- Direct Influence
- Lobbying
- Campaign contributions
- Policy research funding
- Indirect Influence
- Industry associations
- Public-private partnerships
- Economic leverage
Corporate Policy Impact
Key Areas of Influence
- Regulatory Policy
- Industry standards
- Compliance frameworks
- Environmental regulations
- Economic Policy
- Tax policy
- Trade agreements
- Labor regulations
Interaction of Actors
-
Policy Domain
-
"A substantive area of public policy such as health care, education, or the environment." - Stone
- A policy domain can be a single policy or a group of related policies
- an area where actors compete and compromise
-
"A substantive area of public policy such as health care, education, or the environment." - Stone
Interaction of Actors
-
Policy Community
- The group of actors who are involved in a particular policy domain.
Interaction of Actors
-
Subgovernment
- "A network of groups within the American political system that exercise a great deal of control over specific policy areas." - Stone
- An issue network is a more open version of a subgovernment.
- Open to numerous actors, interest groups, think tanks, corporations, individuals, etc.
- Often consists of a few key actors or advocacy coalitions.
Interaction of Actors
-
Iron Triangle
-
"A stable, mutually beneficial political relationship among a congressional committee (or subcommittee), an administrative agency, and organized interests concerned with a particular policy domain." - Stone
- Example: The House Committee on Energy and Commerce, the EPA, and the American Petroleum Institute
- An iron triangle is more closed than an issue network.
-
"A stable, mutually beneficial political relationship among a congressional committee (or subcommittee), an administrative agency, and organized interests concerned with a particular policy domain." - Stone
Iron Triangle
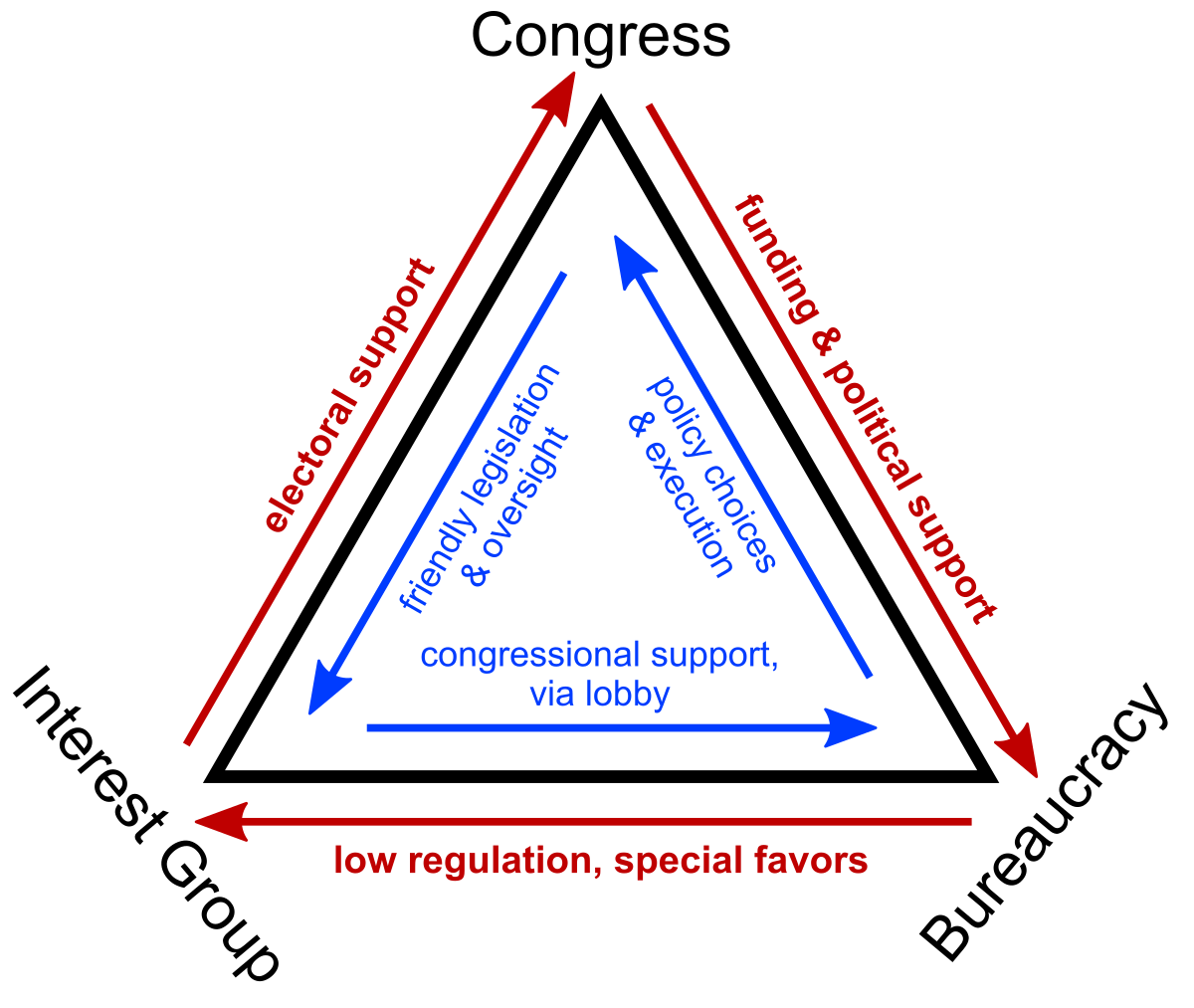
Interaction of Actors
-
Policy Regime
- "A loosely formed governance structure formed by a policy community around a particularly broad policy domain." - Birkland
-
- When a policy domain is broad and spans boundaries of various types, the actors, coalitions, interests, and agencies form a policy regime—a loose governance structure.
Conclusion
- Unofficial actors play critical roles in the policy process
- Understanding their interactions is essential for policy analysis
- Media, parties, interest groups, think tanks, corporations, and individuals shape policy outcomes
- Complex dynamics and power structures influence policy decisions
Next Time
- Individuals in the Policy Process
- King's Letter from the Birmingham Jail